Cauca Department
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (March 2009) |
Department of Cauca
Departamento del Cauca | |
|---|---|
 Puracé volcano seen from Popayán | |
| Motto(s): Por el Derecho a la Diferencia (Spanish: For the Right to a Difference) | |
 Cauca shown in red | |
 Topography of the department | |
| Coordinates: 2°27′N 76°37′W / 2.450°N 76.617°W | |
| Country | |
| Region | Andean Region/Pacific Region |
| Department | 1824 |
| Province | 1537 |
| Capital | Popayán |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Elías Larrahondo Carabalí (2020-Present) |
| Area | |
• Total | 29,308 km2 (11,316 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 13th |
| Population (2018)[1] | |
• Total | 1,464,488 |
| • Rank | 11th |
| • Density | 50/km2 (130/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Total | COP 25,768 billion (US$ 6.1 billion) |
| Time zone | UTC-05 |
| ISO 3166 code | CO-CAU |
| Municipalities | 41 |
| HDI (2019) | 0.719[3] high · 25th of 33 |
Cauca Department (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈkawka], Spanish: Departamento del Cauca) is a department of Southwestern Colombia. Located in the southwestern part of the country, facing the Pacific Ocean to the west,[4] the Valle del Cauca Department to the north, Tolima Department to the northeast, Huila Department to the east, and Nariño Department to the south. Putumayo and Caqueta Departments border the southeast portion of Cauca Department as well. It covers a total area of 29,308 km2 (11,316 sq mi), the 13th largest in Colombia. Its capital is the city of Popayán. The offshore island of Malpelo belongs to the department. It is located in the southwest of the country, mainly in the Andean and Pacific regions (between 0°58′54″N and 3°19′04″N latitude, 75°47′36″W and 77°57′05″W longitude) plus a tiny part (Piamonte) in the Amazonian region. The area makes up 2.56% of the country.
Administrative Division
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (July 2023) |
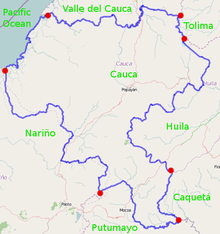
Cauca Department is divided into 42 municipalities, 99 districts, 474 police posts and numerous villages and populated places. The municipalities are grouped into 27 circles and 29 notaries: a circle-based registration in Popayán and eight sectional offices based in Bolívar, Caloto, Puerto Tejada, Santander de Quilichao, Patia, Guapi and Silvia, makes up the judicial district of Popayán. This district possesses 8 judicial circuit seats in Popayán, Bolívar, Caloto, Guapi, Patia, Puerto Tejada, Santander de Quilichao and Silvia. The department makes up the constituency of Cauca.
Physiography
[edit]The relief of the territory of the department of Cauca belongs to the Andean system at the macro level seven distinguishing morphological units:
- the Pacific Plate
- the Pubenza Valley
- the Western Cordillera
- the Central Cordillera
- the Popayán Plateau
- the Colombian Massif
- the Patía Valley
- a small sliver of the Amazon Basin
The Pacific Plate comprises two sectors, firstly the alluvial coastal belt or platform characterized by low, swampy, mangrove forest with many rivers estuaries subject to the ebb and flow of tides, the remainder is a plain or hills comprising the western slopes of the western cordillera.
The western cordillera in Cauca extends from southwest to northeast. Among the most important landmarks are the blade of Napí, the hills of Guaduas, Munchique, and Naya, and the Cauca River Valley. The central mountain range crosses the department from south to north; relevant landmarks include Sotará Colcano, Petacas Nevado del Huila, and the departmental boundary.
The highlands of Popayán, sandwiched between the Western and Central Cordilleras, is seen as a landmark within the plateau of the hill of La Tetilla. Among the most representative landmarks of the Colombian Massif, shared with the department of Huila, are the Páramo del Buey, the volcanoes of Cutanga and Puracé, the peak of Paletará, and the Sierra Nevada of Coconucos. Patia Valley, where the Patia River runs north–south and framed by the Central and Western mountain ranges, extends into Nariño Department. The Amazonian salient corresponds to the so-called Bota Caucana, through which flows the Japurá River.
Colombian Massif
[edit]
The Colombian Massif, also called the Nudo de Almaguer, is a mountainous section of Andean natural region formed by the convergence of two major mountain ranges, the Central and the Eastern cordilleras. The massif extends through the departments of Cauca, Huila, and Nariño. Towards the south, the Colombian Massif is continued by the Pasto Massif and towards the north it diverges forming the Central and Eastern Andes. The Colombian Massif is a strategic national and international level, given its significance for water production, biodiversity and ecosystems, an area that represents a special conformation of the regions with more potential for development in Colombia.
Hydrography
[edit]Cauca Department can be divided into the following hydrographic regions:
- The Cauca river system, consisting of five major basins: Alto Cauca, Pacific, Alto Magdalena, Patia and Caqueta. Alto Cauca, the most important, is formed by the Cauca River and its tributaries: Palo, Guengué, Negro, Teta, Desbaratado, and Quilichao, Mondomo, Ovejas, Pescador, Robles, Piedras, Sucio, Palacé, Cofre, Honda, Cajibío, Piendamó, Tunia, Molino, Timbío and Blanco.
- Patia basin, consists of the Patia River and its tributary rivers Guachinoco, Ismita, Bojoleo, El Guaba, Sambingo and Mayo.
- Outside the Patia basin, the Pacific slope is mainly drained by the rivers Guapi, Timbiquí, Saija and Micay.
- Alto Magdalena, whose main river is the Páez River which is fed by the rivers: San Vicente, Moras, Ullucos, Negro y Negro de Narvaez, and the streams: Toez, Símbola, Salado, Gualcar, Gallo, Macana, Honda and Totumo.
- Caquetá basin, consists of the Caquetá River into which the rivers Cusiyaco, Cascabelito, Verdeyaco, Mandiyaco, Fragua, Cascabel, Curiaco and Pacayaco flow.
Gorgonilla and Gorgona islands are located in the Pacific Ocean and belong to Cauca Department.
Economy
[edit]| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1938 | 356,040 | — |
| 1951 | 391,509 | +10.0% |
| 1964 | 607,197 | +55.1% |
| 1973 | 582,709 | −4.0% |
| 1985 | 857,751 | +47.2% |
| 1993 | 1,127,678 | +31.5% |
| 2005 | 1,268,937 | +12.5% |
| 2018 | 1,464,488 | +15.4% |
| Source:[5] | ||
The Cauca economy is based primarily on agriculture and livestock production, forestry, fishing and trade. Agriculture has been developed and modernized in the northern department, with the main crops being sugar cane, cane panela, conventional maize, rice, corn tech, banana, agave, yucca, potatoes, coconut, sorghum, cocoa, groundnut, and palm.
In the Pacific region is extracted gold, silver and platinum. Other non-precious minerals that are exploited are sulfur, asbestos, limestone, talc, gypsum and coal. The manufacturing industry is located in Popayán, Santander de Quilichao, Puerto Tejada with factories of food, beverages, dairy products, paper, packaging, wood processing, sugar industry and paper processing for export. The main centers of commercial activity are Popayán, Santander de Quilichao, Patia, Puerto Tejada, Piendamó and Corinto.
Municipalities
[edit]- Almaguer
- Argelia
- Balboa
- Bolívar
- Buenos Aires
- Cajibío
- Caldono
- Caloto
- Corinto
- El Tambo
- Florencia
- Guapi
- Inzá
- Jambaló
- La Sierra
- La Vega
- López de Micay
- Mercaderes
- Miranda
- Morales
- Padilla
- Páez
- Patía
- Piamonte
- Piendamó
- Popayán
- Puerto Tejada
- Puracé
- Rosas
- San Sebastián
- Santander de Quilichao
- Santa Rosa
- Silvia
- Sotará
- Suárez
- Sucre
- Timbío
- Timbiquí
- Toribío
- Totoró
- Villa Rica
References
[edit]This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (March 2009) |
- ^ "DANE". Archived from the original on 13 November 2009. Retrieved 13 February 2013.
- ^ "Producto Interno Bruto por departamento", www.dane.gov.co
- ^ "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 13 September 2018.
- ^ Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- ^ "Reloj de Población". DANE. Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadísitica. Archived from the original on 16 January 2018. Retrieved 6 July 2017.
External links
[edit]- Official website
 Cauca travel guide from Wikivoyage
Cauca travel guide from Wikivoyage- Territorial-Environmental Information System of Colombian Amazon SIAT-AC website Archived 2020-06-17 at the Wayback Machine